EVERYTHING YOU WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT
Business Analysis
Definitions, Perspectives, Processes, Tools, and Techniques
- Overview
- Principles
- Perspectives
- Process
- Tools
- Techniques
- Training
- FAQ
What is Business Analysis
Learn How to Earn 40% More With CBAP
Business Analysis Principles
A principle can be defined as an underlying fundamental law or concept. Therefore, Business Analysis principles are the basic rules that should be followed to manage changes successfully.
The Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK) does not currently contain an official list of principles for successful change initiatives. However, IIBA’s Agile Analysis Guide does provide 7 principles. They are:
1. See the whole,
2. Think as a customer,
3. Analyze to determine what is valuable,
4. Get real using examples,
5. Understand what is doable,
6. Stimulate collaboration and continuous improvement, and
7. Avoid waste.
Here are 16 Business Analysis Principles we are proposing:
1. Set clear and objective goals and outcomes. A change without clear objectives is bound to fail.
2. Engage stakeholders continuously. Stakeholder needs are the reason for the change. Stakeholders must work together throughout the project.
3. Include all relevant stakeholders. Successful change management requires all key stakeholders to be included in the change initiative.
4. Think holistically. Changes affect people, process, and technology. All 3 aspects are essential for successful change.
5. Adapt vigorously. Welcome change for competitive advantage.
6. Deliver iteratively. Deliver frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter time scale.
7. Encourage change adoption. Motivate stakeholders to change for better.
8. Communicate frequently. The most efficient and effective communication is face-to-face conversation.
9. Measure continually. Better outcomes are the primary measure of progress.
10. Work sustainably. Stakeholders should be able to maintain a constant pace indefinitely.
11. Pursue excellence. Continuous attention to excellence in business analysis skills, processes, and tools.
12. Avoid waste. The art of maximizing the number of requirements not done is essential.
13. Reflect regularly. Stakeholders reflect on how to become more effective, then change behavior accordingly.
14. Organize dynamically. Best solutions emerge from self-organizing teams.
15. Manage risks proactively. Identify, analyze, and mitigate risks
16. Define roles and responsibilities clearly. Set clear expectations from all key stakeholders.
Learn How to Earn 40% More With CBAP
Business Analysis Perspectives
|
Business analysis is a vast topic. It can be conducted from multiple perspectives. Following is a list of perspectives which by no means is exhaustive. 1. Enterprise strategy analysis |
.webp?width=550&height=309&name=Flavors-of-business-analysis-1%20(1).webp)
|
Learn How to Earn 40% More With CBAP
Business Analysis Process
The set of tasks and techniques that are used to perform business analysis are defined in the Guide to the Business Analysis Body of Knowledge® (BABOK® Guide). We have listed all the tasks in BABoK in a subsequent section. Unfortunately, BABoK does not give a definite business analysis process definition. It is rightly so because the situations are different, organizations are different, needs are different. Trying to propose a business analysis process in such varied conditions can really be a nightmarish approach.
At the same time, applying Pareto’s principle, it will be prudent to say that in about 80% of the situations, we can propose a solid business analysis process. For remaining 20% cases, of course, we need expert guidance and need to design custom process. We are proposing a 10-step approach to business analysis. We propose following 7 steps business analysis process.
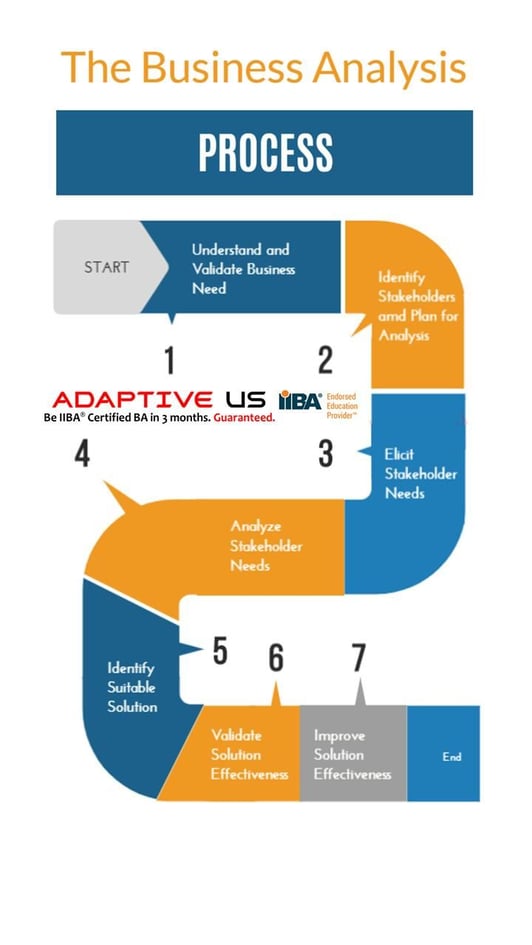
1. Plan, Engage, and Monitor
There are certain activities which run across the business analysis life cycle. This is numbered as 0 as it is the foundation for the remaining phases. Phase 0 will involve continuous planning, monitoring, engaging stakeholders, managing issues, risks, requirements, traceability. For every phase, we should perform an appropriate level of planning and monitoring.
2. Understand Project Context, Objectives, and Scope
Often business analysts are expected contribute as soon as possible towards project delivery. Often, the project may have started already, or a phase may be completed. As business analysts, it’s our job to clarify the business and project objectives as quickly as possible. Investing some time, whether that’s a few hours or few days, to get oriented will ensure we are not only moving quickly but also competent, effective, and confident contributor for the project.
3. Elicit Requirements
Plan to understand the process and expectations in detail from various stakeholders to understand their expectations from the solution. Identify stakeholders who are in best position to provide the requirements. Choose appropriate techniques to conduct elicitation activities.
4. Manage Requirements
Not all stakeholder expectations can be met given the organizational constraints. We need to understand which requirements are critical and feasible.
6. Document Requirements
Detailed requirements provide the implementation team with the information they need to implement the solution.
7. Define solution options
Define suitable solution options to meet business and stakeholder needs.
8. Evaluate and Improve Solution Performance
A track record of successful projects creates significant positive momentum within an organization. So, if we need to assess the value created by the solution.
Learn How to Earn 40% More With CBAP
Business Analysis Tools
Commonly used business analysis tools are:
1. Microsoft Visio
2. Atlassian Jira
3. Balsamiq
4. Lucid Chart
5. BizAgi BPM
Here are a brief descriptions about them:
-
Microsoft Visio: Microsoft Visio is a versatile diagramming tool that enables users to create a wide range of diagrams, from flowcharts and organizational charts to floor plans and network diagrams. With an intuitive interface and a vast library of shapes and templates, Visio makes it easy for users to visualize complex information and communicate ideas effectively. It offers features such as data connectivity, collaboration tools, and integration with other Microsoft Office applications, making it a valuable tool for professionals in various fields including business analysis, project management, and engineering.
-
Atlassian Jira: Atlassian Jira is a popular project management tool designed to help teams plan, track, and manage their work efficiently. It offers powerful features such as issue tracking, agile project management, customizable workflows, and real-time collaboration, enabling teams to stay organized and focused on delivering high-quality results. Jira's flexibility makes it suitable for various project methodologies, including Scrum, Kanban, and waterfall. With its extensive integration capabilities and ecosystem of add-ons, Jira provides teams with the flexibility to adapt to their unique workflows and scale as their needs evolve.
-
Balsamiq: Balsamiq is a rapid wireframing tool that allows users to create low-fidelity mockups of software interfaces quickly and easily. Its simple drag-and-drop interface and library of pre-built UI components enable users to visualize their ideas and iterate on designs rapidly. Balsamiq's focus on simplicity and speed makes it ideal for brainstorming, prototyping, and gathering feedback early in the design process. Its sketch-style wireframes help teams communicate ideas effectively and facilitate collaboration between designers, developers, and stakeholders, ultimately leading to better-designed products and user experiences.
-
Lucidchart: Lucidchart is a cloud-based diagramming tool that enables users to create professional-quality diagrams and visualizations easily. It offers a wide range of templates and shapes for creating flowcharts, network diagrams, org charts, and more, making it suitable for various industries and use cases. Lucidchart's collaborative features allow teams to work together in real-time, comment on diagrams, and track changes, fostering communication and alignment across distributed teams. With integrations with popular productivity and project management tools, Lucidchart streamlines workflows and helps teams bring their ideas to life more efficiently.
-
Bizagi BPM: Bizagi BPM is a business process management platform that helps organizations streamline and automate their business processes. It offers powerful tools for process modeling, execution, and optimization, allowing businesses to visualize, analyze, and improve their workflows continuously. With its user-friendly interface and drag-and-drop editor, Bizagi BPM enables business analysts and process owners to design and simulate processes easily, without the need for coding. Its advanced features, such as rule engines, integration capabilities, and analytics, empower organizations to automate repetitive tasks, reduce errors, and enhance operational efficiency, ultimately driving business agility and innovation.
Learn How to Earn 40% More With CBAP
Business Analysis Techniques
There are hundreds of techniques which business analysis professionals use. The most common ones are:
Functional decomposition
Functional decomposition breaks down a large aspect (processes, functional areas, deliverables, scope, or problems) into smaller aspects, as independent as possible, so that work can be assigned to different groups. This reduces complexity of analysis.
Estimation
Estimation techniques are used for better understanding of possible range of costs and efforts associated with any change.
Interface analysis
An interface is a connection between 2 components or solutions. Identify interfaces and interactions between solutions and/or solution components.
Organizational modelling
Org. modelling describes roles, responsibilities, and reporting structures that exist within an organization, and aligns those structures with organization’s goals. Visual representations of organizational units.
Stakeholder list, map, or personas
Identify stakeholders affected by a proposed initiative or share a common business need, level of decision-making authority, authority within domain and organization, attitude/ interest towards change, and business analysis work.
Scope modelling
Describe scope of analysis or scope of a solution. They serve as a basis for defining and limiting scope of business analysis and project work
Brainstorming
One or group of stakeholders deliberate on an idea to produce numerous new ideas in a non-judgmental environment, and to derive themes for further analysis.
Workshops
Requirements workshop, also known as JAD (Joint application design) session, is a highly productive focused event attended by carefully selected key stakeholders, and Subject Matter Experts for a short, intensive period (typically 1 or a few days).
Focus groups
Elicit ideas, impressions, preferences, and needs and attitudes from pre-qualified individuals about a specific product, service, or opportunity in an interactive group environment. Guided by a moderator. Typically 1 to 2 hours with 6-12 attendees.
Collaborative games
Uses game playing techniques to collaborate in developing common understanding of a problem or a solution. Involves strong visual or tactile (activities) elements such as moving sticky notes, writing on whiteboards, or drawing pictures.
Interviews
Most common form of elicitation technique where interviewers ask questions to stakeholders. Effective interviewers control discussions understand needs from ALL stakeholders, probe deeper when needed and ensure completeness of answers.
Observation
Elicit information by observing activities and their contexts.
Survey or questionnaire
Administers a set of written questions to stakeholders and Subject Matter Experts. Survey can elicit information from many people, sometimes anonymously, in a relatively short period of time. Can collect information about customers, products, work practices and attitudes. Alternatively, respondents are provided with a series of statements and asked for their level of agreement.
Document analysis
Elicit Business Analysis information, by examining materials describing business environment or organizational assets. Document analysis helps in understanding context of a business need or understanding how existing solutions are implemented. Based on Business Analysis information being explored, purpose, scope, and topics to be researched are determined.
Benchmarking and market analysis
Benchmarking compares org. practices against best-in-class practices from competitors, government, industry associations or standards. Market analysis understands customers’ needs, factors influencing purchase decisions, and studies competitors.
Prototyping
Provides an early model of final result, widely used for product design. Details UI requirements and integrates them with other requirements such as use cases, scenarios, data, and business rules. Stakeholders often find prototyping to be a concrete means of identifying, describing, and validating their interface needs. Prototypes can discover desired process flow and business rules.
Glossary
Comprises of key terms relevant to a business domain to provide a common understanding of terms. Contains definitions and synonyms. Needs to be organized and be accessible to all stakeholders.
Mind Map
Articulates and captures ideas in a non-linear (tree) structure. Ideas are grouped as topics, sub-topics, further sub-sub-topics. Mind maps use words, images, color, and connections to structure thoughts, ideas, and information.
Backlog management
Backlogs record, track and prioritize remaining work items. Backlog management is a planned approach to manage remaining work for project. In managed backlogs, items at top have highest business value and priority. Backlog items can be user stories, use cases, defects, CRs, risks etc.
Business rules analysis
Business policies dictate actions of an enterprise and people in it by broadly controlling, influencing, or regulating them. Business rules serves as a criterion for guiding behavior and making decisions in a specific, testable manner.
Lessons learned
Discusses and documents successes, failures and improvement recommeDendations for future phases or projects. Can include any format or venue that is acceptable to key stakeholders. Can be formal facilitated meetings or informal.
Prioritization
Provides a framework for stakeholder decisions to understand relative importance of requirements. Importance may be based on value, risk, difficulty of implementation etc.
Reviews
Communicate, verify, and validate content of work products, formally or informally. Communicate review objectives in advance to participants.
Item tracking
Captures and assigns responsibility for issues and stakeholder concerns. Items can refer to actions, assumptions, constraints, dependencies, defects, enhancements, and issues.
Balanced scorecard
A strategic planning and management tool to measure org. performance beyond traditional financial measures aligned to organization's vision and strategy.
Business capability analysis
Capability maps provide a graphical view of capabilities. Capabilities describes ability of an enterprise to act on or transform something that helps achieve a business goal or objective. Capabilities describe outcome of performance or transformation, not how it is performed.
Business cases
Formally or informally, justify investments based on estimated value compared to cost. Spend time and resources on business case proportional to the size and importance of its potential value. Business cases do not provide intricate details.
Business model canvas
Comprises 9 building blocks describing how an organization intends to deliver value. As a diagnostic tool, use elements of the canvas as a lens into current process or system of business, especially wrt relative amounts of energy, time, and resources currently invested in various areas.
Decision analysis
Supports decision-making in complex, difficult, or uncertain situations. Examines and models possible consequences of different decisions. One of the common scenario for decision analysis is Buy vs. Build analysis.
Decision modeling
Shows how repeatable business decisions are made using data and knowledge.
Financial analysis
Explore financial aspects (benefits and costs) of an investment.
Risk analysis and management
Identify, analyze, and evaluate uncertainties that could negatively affect value, develop and manage way of dealing with risks.
SWOT analysis
SWOT is an acronym for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. A framework for strategic planning, opportunity analysis, competitive analysis, business, and product development.
Concept modelling
Organizes business vocabulary, usually starting with glossary.
Data dictionary
Standard definitions of primitive data elements, their meanings, allowable values, how those elements combine into composite data elements. Used to manage data within a solution’s context, often used along with ER diagrams.
Data modelling
Data models describe entities, classes or data objects relevant to a domain, their attributes and relationships among them.
Data flow diagrams
Show transformation of data from (data source such as external sources, activities and destination). Data used in DFDs should be described in a data dictionary. Highest level diagram (Level 0) is context diagram represents the entire system.
Process modelling
Graphical model to describe sequential flow of activities. A system process model defines sequential flow of control among programs or units within a computer system. A program process flow shows sequential execution of program statements within a software program.
Sequence diagrams
Sequence diagrams (also known as event diagrams) model logic of usage scenarios, by showing information (also known as stimuli, or message) passed between objects during execution of a scenario.
State modelling
State models (also sometimes called a process or system transition model) describe and analyze different possible states (formal representation of a status) of an entity within a system, how that entity changes from one process or system to another and what can happen to entity when it is in each state.
User stories
User stories are a brief textual description, typically 1 or 2 sentences, of functionality that users need from a solution to meet a business objective. User story describes actor (who uses story), goal they are trying to accomplish, and any additional information to be critical to understanding scope of story.
Use cases and scenarios
Scenarios, and use cases describe how actors (a person or a system) interacts with a solution to accomplish one or more of that person or systems goals.
Non-functional requirements analysis
Examines requirements for a solution that define how well functional requirements must perform. Also known as quality attributes or quality of service requirements. Expressed in textual formats as declarative statements or in matrices.
Roles and permissions matrix
Ensure coverage of activities by denoting responsibility, to identified roles, and to discover missing roles.
Acceptance and evaluation criteria
Acceptance criteria describe minimal set of requirements to be met for a solution to be worth implementing, also known as Must Have requirements. Typically used when evaluation only one possible solution and is expressed as pass or fail. Must be testable.
Metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs)
Measure performance of solutions, solution components and other matters of interest to stakeholders. A metric is a quantifiable level of an indicator to measure progress. A target metric is objective to be reached within a specified period.
Process analysis
Analyzes processes for their effectiveness, efficiency, and identifies improvement opportunities.
Root cause analysis
Identify and evaluate underlying causes of a problem, looking into causes occurring due to people, physical or organizational effects.
Vendor assessment
Assess ability of a potential vendor to meet commitments wrt delivery and consistent provision of a product or service.
Data mining
Finds useful patterns and insights from large amounts of data, usually resulting in mathematical models. Utilized in either supervised (user poses a question) or unsupervised (pure pattern discovery) investigations.
MOST
Most is a short form of Mission, Objectives, Strategies. It allows business analysts to perform thorough internal analysis of what is the aim of an organization to achieve and how to tackles such issues.
PESTLE
Pestle stands for (Political, Economic, Sociological, Technological, Legal, and Environmental). This model helps business analysts to evaluate all the external factors which can possibly impact their organization and determine how to address them.
SWOT
SWOT is a full form of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This technique helps we to find areas of both strength and weakness. It also allows for the proper allocation of resources.
MoSCoW
Must or Should, Could or Would process is a long-form of MosCoW. This technique allows prioritization of requirements by presenting a framework in which every individual requirement should be evaluated relative to the others.
CATWOE - Customers, Actors, Transformation Process, World View, Owner, and Environmental
This technique helps us to recognize processes that may be affected by any action the business undertakes.
The 5 Whys
This technique is a backbone of both Six Sigma and business analysis techniques. It consists of leading questions that allow business analysts to single out the root cause of an issue by asking why such a situation arises.
Six Thinking Hats
This process helps us to consider alternate perspectives and ideas.
Learn How to Earn 40% More With CBAP
Business Analysis Training

Business analysis learning can be expedited by undergoing a formal training.
Many colleges, universities, professional training institutes provide structured training on business analysis.
Adaptive US provides both theory training through it's Entry Certificate in Business Analysis training and skill training through it's Inner Circle program.
Learn How to Earn 40% More With CBAP
Business Analysis FAQ
What is business analysis?
Business analysis is the practice of enabling positive change in an enterprise/ organization/ process/ product by defining needs (Strategic Problems or Opportunities) and recommending solutions that deliver value (benefits – costs) to stakeholders (users, owners, regulators).
What is the difference between business analysis and business analytics?
Business analysis is focused on developing solutions for business problems or opportunities. Business analytics is focused on obtaining insights on business performance based on data.
What are the key components of business analysis?
Key components of any business are : Customers, Needs, Product/Service, Competition and Regulation.
What exactly does a business analyst do?
Business analysts analyze any business or organization, document systems and processes, identifying significant problems and opportunities, and devising solutions. Business analysts go by hundreds of job titles, including: Business Architect.
What are the 5 C's in business analysis?
The 5 C's consist of five aspects that are important to analyze for a business. The 5 C's are company, customers, competitors, collaborators, and climate.
What are the 7 stages of business analysis?
The Seven Steps of Business Analysis provides a systematic for defining a business process, understanding how to identify improvement opportunities, how to design meaningful performance measures, how to analyze problems in a systematic way, solve business problems.
What are business analysis tools?
Business analysis tools are types of software that are used manage requirements such as Jira, model processes, such as MS Visio, retrieve data from one or more business systems and combine it in a repository, such as a data warehouse, to be reviewed and analyzed.
Is business analyst an IT job?
Business analyst role is very popular in the IT sector, but it can be outside IT as well. This role could focus on business process improvement in any sector.
What are the 6 pillars of business analysis?
The six core concepts / pillars are: Change, Need, Solution, Stakeholder, Value, and Context.
Is SQL required for business analyst?
SQL is an essential tool for business data analysis because it allows analysts to manipulate and query large datasets with ease. SQL is used to extract and manipulate data from databases.
Will AI make business analysis redundant?
Some parts of routine business analysis will be automated by AI. However, complex problems and managing the change will require human intervention.
Do I Need an MBA to Be a Business Analyst?
Having an MBA degree helps. Many business analysts come with graduate degree, some even with high school degree. The spirit to learn makes a great difference.
Do I need programming knowledge to become a BA?
Some basics of programming is helpful but not necessary for business analysts.
Is business analysis only about documentation?
Business analysts do document many aspects about the business but it is just 1 aspect of 10+ critical aspects that BAs manage, such as stakeholder management, data analysis, problem solving approaches, training stakeholders etc.
What are career paths for Business analysts?
Business analysts can become BA managers, Product owners, Account managers, leading to CXO roles in the organization.
What is agile business analysis?
Agile business analysis refers to conducting business analysis in agile development approach.



