Organizational Modeling - What, Why, and How
Blog Summary (in 200 words)
This blog delves into organizational modeling, explaining its significance, purpose, and implementation. Organizational modeling is a technique used by business analysts to understand the structure, functions, and interactions within an organization.
The blog outlines the importance of organizational modeling in various contexts, including business process improvement, organizational change management, and system implementation. By visualizing the organizational structure and relationships, BAs can identify inefficiencies, redundancies, and areas for improvement.
The process of organizational modeling involves several steps, starting with gathering information about the organization's structure, processes, and stakeholders. BAs then use modeling techniques such as organizational charts, process maps, and stakeholder matrices to represent these aspects visually.
The blog emphasizes the benefits of organizational modeling, including improved decision-making, better alignment of resources, and enhanced communication across the organization. It also highlights the challenges associated with organizational modeling, such as obtaining accurate data and ensuring stakeholder buy-in.
Overall, organizational modeling is a valuable technique for business analysts to gain insights into the complexities of an organization and drive positive change. By understanding the "what, why, and how" of organizational modeling, BAs can effectively facilitate process improvements and organizational transformations.

Detailed Blog
Are you familiar with the term "organizational modeling"? It's a powerful tool for business analysts and organizations, allowing them to create a structural framework to enhance their operations. By developing an effective organizational model, businesses can streamline processes, optimize resources, and achieve greater success in achieving their goals.
In this blog post, we'll explore what organizational modeling is all about - its history, different types of models available today - and how you can develop one for your organization! So, let's dive right in!
What is an organizational model?
An organizational model is a framework or structure that represents the different components of an organization, such as its employees and departments. It provides a clear understanding of how an organization functions and manages its resources to achieve its goals. It defines the relationships between different parts of the organization and establishes lines of communication and decision-making. It outlines the blueprint for how work gets done within an organization.
Organizational models have been around for centuries, with various forms being developed throughout history. From military-style hierarchies to more modern matrix structures, many types of organizational models are available today.
The purpose behind developing an organizational model is to create efficiency in operations by streamlining workflows while remaining agile enough to adapt quickly to changes in business needs. An effective organizational model, incorporating best practices, can also help businesses reduce costs while improving productivity and competitiveness. A well-designed corporate model is essential for any business looking to grow and succeed in today's fast-paced world. Leveraging the right approach based on your specific needs as a business analyst or consultant through proper business analysis techniques can drive improvements in all aspects of your company's performance, from financial management practices down to employee engagement levels
History of organizational model
The history of organizational models dates back to the early 20th century when businesses were growing and becoming more complex. The traditional hierarchical model, which includes a defined chain of command, was no longer effective, and a new way of organizing people was needed.
One of the earliest pioneers in organizational modeling was Frederick Winslow Taylor, who developed the scientific management approach. Taylor's goal was to improve efficiency by breaking down tasks into smaller parts and optimizing each one.
In the 1930s, Elton Mayo conducted experiments at Western Electric's Hawthorne Works that led to the human relations movement. He discovered that productivity wasn't solely based on working conditions; social factors such as employee morale also played a role. During the post-World War II era, many organizations began adopting bureaucratic models inspired by Max Weber's work. These models utilized strict rules and regulations to ensure consistency across departments but were criticized for being too rigid.
As time passed, more flexible models emerged, such as matrix structures which allowed individuals from different functional areas to collaborate on projects. Today, organizations are still experimenting with new ways of organizing people in response to changes in technology and business needs.
Why model organizations?
Modeling organizations is an essential process for any business analyst or strategist. It helps in understanding the structure and functions of an organization to identify weaknesses, strengths, opportunities, and threats. By modeling different aspects of the company's operations and management, a business analyst can help managers make informed decisions that maximize profits.
A major advantage of organizational modeling is its ability to provide a clear picture of how different departments/functions/units/lines of businesses within a company interact. With such insight, stakeholders at all levels can better understand how various roles contribute towards achieving the same objectives. This allows firms to stay competitive in today's fast-paced economic environment by adapting quickly, when necessary, based on changing business environments.
Different types of organizational models
Businesses can adopt different types of organizational models depending on their structure and goals. One type is the functional organizational model, which groups employees based on specialty, function, or skill. This helps improve efficiency as it allows employees to focus on specific tasks and responsibilities, which is an important step of the process in management.
Another type is the market-oriented organizational model, which focuses on customer needs and demands. In this model, departments are organized around product lines or customer segments rather than functions. This allows for better customer service and a more tailored marketing approach.
A third option is the matrix organizational model, which combines aspects of both the functional and market-oriented models. In this model, teams are formed around specific projects or initiatives, with members from various departments working together towards a common goal.
Choosing the right organizational model depends on factors such as company size, industry niche, and business objectives. It's essential for businesses to carefully evaluate their options before deciding to implement a new business strategy to ensure they choose an effective structure that will help them succeed in today's competitive landscape.
Functional organizational model
The functional organizational model is a common organizational structure where employees are grouped according to their skills or job roles. This type of model is used in many organizations, especially those with well-defined functions and tasks.
In this model, each department focuses on specific functions such as finance or marketing. The departments have clear goals and objectives that align with the organization's overall mission. This allows for better team coordination and helps ensure everyone is working towards the same goal.
One of the main advantages of a functional organizational model is efficiency. Because employees are grouped based on their skills, they can specialize in their area of expertise and become more productive over time. Additionally, departments can share resources which reduces costs for the organization.
However, there are also some drawbacks to this type of model. Communication between departments may be limited, which can lead to silos forming within the organization. It may also be difficult to make changes quickly since each department has established procedures and protocols.
Understanding different types of organizational models is important for business analysts who work with clients looking to improve their internal structures. The functional organizational model has pros and cons, but it remains one popular option among businesses today.
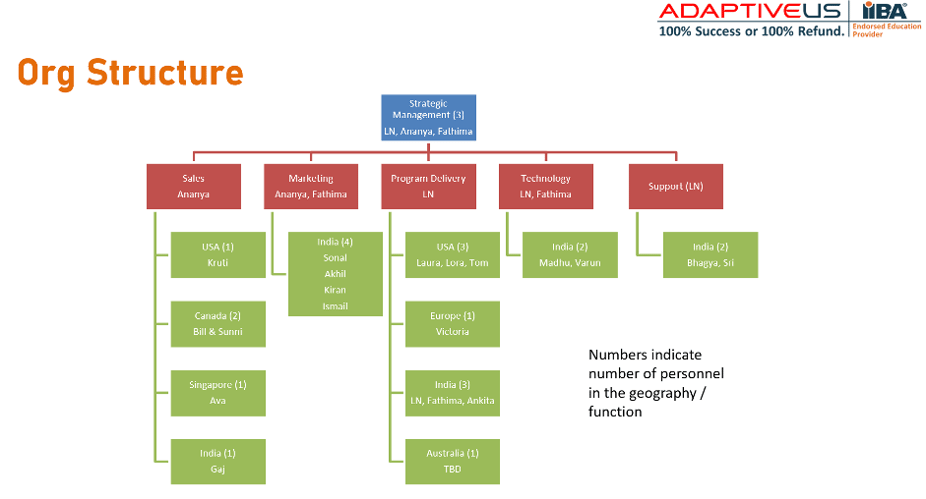
Adaptive US Org. Structure
Market-oriented organizational model
The market-oriented organizational model places a strong emphasis on customer needs and preferences. In this model, the company's structure is designed to be flexible, allowing it to respond quickly to changes in the marketplace.
This type of organizational model is particularly well-suited for companies operating in highly competitive industries where customers have many choices and are constantly demanding new products or services.
One of the key features of a market-oriented organizational model is its focus on a specific domain or geography, thus ensuring better customer satisfaction. Another important aspect of this model is cross-functional collaboration. Departments such as marketing, sales, and product development work together closely to ensure that all aspects of the business are aligned with customer needs.
The market-oriented organizational model has proven successful for many companies looking to stay ahead in today's fast-paced business environment. By prioritizing customer-centricity and agility, these organizations are better equipped to adapt quickly and succeed in an ever-changing marketplace.
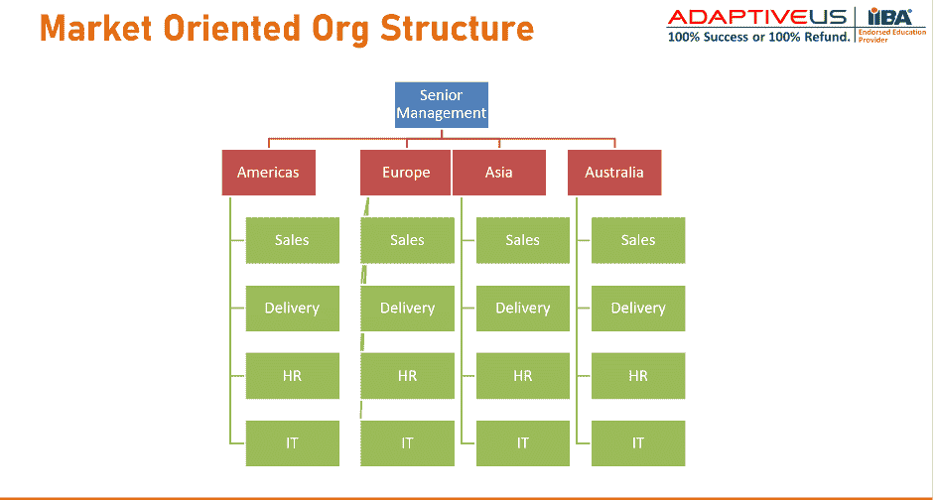
Example of Market-Oriented Org Structure
Matrix organizational model
The matrix organizational model is a combination of functional and market-oriented models. In this model, employees are grouped by both function and product or project. This means that an employee may have two lines of reporting - one who oversees their functional responsibilities and another who oversees their project work. This can create challenges with conflicting priorities and communication difficulties.
However, the matrix model also allows for more flexibility in responding to market or business environment changes. It encourages cross-functional collaboration and can lead to more innovative solutions.
One key aspect of implementing a successful matrix organizational model is ensuring clear communication channels between different teams and departments. A strong emphasis on teamwork, accountability, and alignment around common goals is also crucial. While the matrix structure may not be suitable for every organization or situation, it has potential benefits for those willing to navigate its complexities effectively.
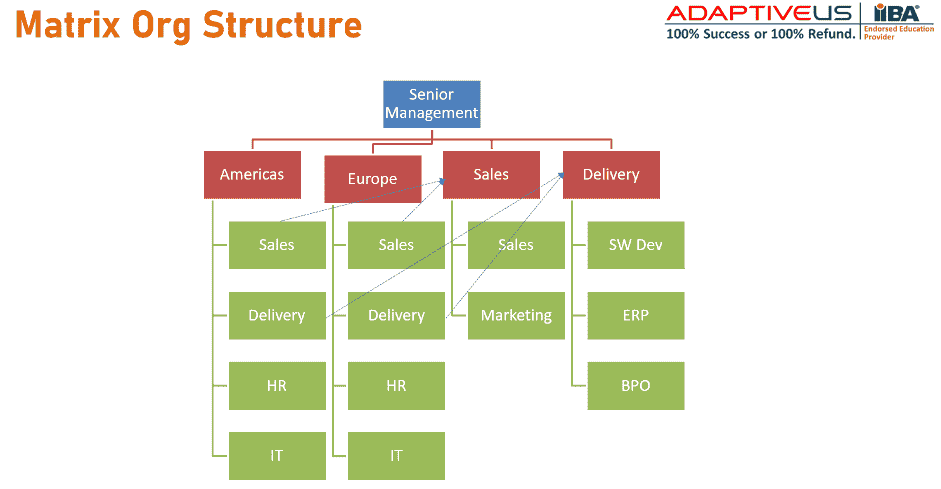
Example of Matrix Org Structure
Diagnostic models
Diagnostic models in organizational design help identify areas for improvement and change within a company. By analyzing aspects like structure, culture, and processes, these models offer insights to enhance overall effectiveness. They assist in pinpointing issues in the chain of command, workflow, and alignment, guiding the development of focused action plans. Through frameworks like McKinsey's 7S organizational design Model and Weisbord's Six Box Model, organizations can diagnose and address challenges to achieve optimal performance.
McKinsey’s 7S Design Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model focuses on alignment within organizations, considering strategy, structure, systems, shared values, skills, style, and staff. Its advantage lies in fostering holistic analysis, enhancing business strategy execution, and aligning all components for success. However, the model might oversimplify complex situations or lack clear cause-effect relationships. It's essential for companies aiming to enhance organizational effectiveness by addressing various aspects simultaneously. This strategic approach can lead to sustained success and improved performance in the competitive business world.
Advantages of the 7s Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model focuses on alignment within organizations, emphasizing strategy, structure, and systems. It ensures all elements work harmoniously to achieve common goals. This model aids in analyzing how various components interact within the company culture. Although it provides a holistic view of the organization, its complexity may pose implementation challenges. Jay Galbraith's Star Model™ highlights strategy, structure, processes, rewards, and people as key elements. This model enhances organizational effectiveness by integrating different departments seamlessly.
Disadvantages of the 7s Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model focuses on organizational effectiveness through seven key elements: strategy, structure, systems, shared values, skills, style, and staff. It provides a holistic view of how these components align within a company. This model emphasizes the interconnectedness among different aspects of an organization and how they impact overall success. Understanding and optimizing these interrelations can lead to improved performance, efficiency, and alignment within the organization.
Jay Galbraith’s Star Model™
McKinsey's 7S Design Model is a comprehensive tool for organizational analysis and change. It emphasizes the interconnectedness between various elements, enabling a holistic view of the organization. One key advantage is its ability to address both hard and soft elements of the organization, promoting alignment and effectiveness. However, a potential drawback lies in its complexity, requiring a deep understanding of the organization, as highlighted in a McKinsey study, to implement successfully. This model is valuable for businesses seeking a structured approach to improve their organizational effectiveness.
Advantages of the Star Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model assesses organizational effectiveness by analyzing seven interconnected elements: strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff, and skills. Its strength lies in its holistic approach, considering both hard and soft elements for organizational success. However, its complexity and time-intensive nature can be challenging for some organizations to implement fully. Integrating this model effectively can drive alignment within the organization, fostering better performance and adaptability to change.
Disadvantages of the Star Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model analyzes organizational alignment, covering strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff, and skills. Its strengths lie in holistic assessment and identifying barriers to change, aiding successful implementation. However, it may oversimplify complexities and lack focus on external factors. The model's flexibility enables tailored solutions, aligning culture with strategy effectively.
Weisbord’s Six Box Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model assesses organizational effectiveness by examining seven interconnected elements. It provides insights into alignment and misalignments within an organization, offering a holistic view to drive change initiatives. This model considers structure, systems, shared values, skills, style, staff, and strategy. By addressing these key areas, organizations can enhance their performance and adaptability in the ever-evolving business world.
Advantages of the Six Box Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model examines various aspects of an organization. Its advantage lies in the comprehensive view it provides, encompassing strategy, structure, and shared values. However, a drawback is the complexity of aligning all seven elements effectively. Jay Galbraith's Star Model™ emphasizes strategy, structure, processes, rewards, and people. This approach enables a holistic understanding of organizational dynamics. Yet, implementation challenges may arise due to the intricate interplay between the model's components.
How to develop an organizational model
Developing an organizational model can be a complex process, but it is necessary for any business that wants to manage its resources and achieve its goals effectively. Here are some steps you can follow when creating an action plan while developing an organizational model.
Identify the key functions and activities of your organization. This will help you determine what roles need to be filled and how they should interact with each other.
Next, consider the size of your organization. A smaller organization may have a more simple structure, while larger organizations may require a more complex matrix or functional model.
Once you have determined the appropriate structure for your organization, identify the specific job responsibilities for each role. This will ensure everyone knows their role in achieving company goals and objectives.
After defining job responsibilities, establish clear communication channels between departments and teams. This includes regular meetings and open lines of communication to ensure everyone is on the same page.
Continuously evaluate your organizational model as your business grows and changes over time. Make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal efficiency and effectiveness in achieving company goals.
Transformational models
Transformational models in organizational design focus on profound shifts within the entire organization. These models aim to bring about culture change and align strategies with business goals. Transformation models require a structured change process, often involving multiple steps and a clear action plan. They are crucial for long-term success and sustainability in today's fast-paced business world. By emphasizing alignment and adaptability, transformational models help companies stay competitive and relevant amidst evolving market dynamics. When aiming for organizational transformation, it's essential to recognize that culture change is not only necessary but also foundational to achieving lasting results.
Transformation Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model offers an insightful approach to analyzing organizational effectiveness. It emphasizes seven interconnected elements: strategy, structure, systems, shared values, skills, style, and staff. This holistic view helps organizations align these components for improved performance. However, a disadvantage of this model is its static nature, which may not adequately address dynamic environments requiring continuous adaptation. Despite this limitation, the 7S Model remains a valuable tool for diagnosing and improving organizational alignment.
Advantages of the Transformation Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model focuses on the alignment of elements within a company to achieve success. Its strengths lie in promoting organizational effectiveness and strategic alignment. However, limitations include complexities in implementation and potential resistance to change. Jay Galbraith's Star Model™ emphasizes various organizational aspects for a holistic approach. This model excels in providing a comprehensive view but may face challenges in adapting to rapidly changing environments. Weisbord's Six Box Model offers a structured framework for assessing organizational performance, enhancing decision-making processes.
Disadvantages of the Transformation Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model examines organizational effectiveness through seven interdependent factors: structure, strategy, systems, style, staff, shared values, and skills. Its strengths lie in holistic insights for aligning strategy with structure and culture, enhancing performance. However, limitations may surface in rigidly defining complex organizational dynamics, overlooking nuances. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages equips businesses with valuable insights to navigate the complexities of organizational design and change seamlessly.
The Congruence Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model assesses organizational effectiveness, focusing on shared values, strategy, structure, systems, staff, skills, and style. It provides a holistic view, highlighting interconnected elements impacting company success. This model emphasizes alignment and mutual reinforcement among various components, ensuring a cohesive organizational strategy. Integrating these factors enhances operational efficiency, leading to improved performance across the entire organization.
Advantages of the congruence model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model is a powerful tool for assessing organizational effectiveness. It examines seven interconnected elements: structure, strategy, systems, shared values, skills, style, and staff. This holistic approach ensures alignment and helps in navigating change successfully within a company. By focusing on these critical areas, organizations can improve their performance and adapt to new business strategies effectively. The 7S model emphasizes the importance of considering all organizational aspects to drive sustainable success.
Disadvantages of the Congruence Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model evaluates organizational effectiveness through seven key elements like structure, systems, and shared values. It provides a holistic view for strategic alignment and change initiatives. While offering a comprehensive analysis, its complexity may pose implementation challenges for some organizations. Jay Galbraith's Star Model™ simplifies the alignment process, focusing on strategy, structure, processes, rewards, and people. This streamlined approach enhances clarity but may oversimplify the reality of organizational dynamics.
The Burke-Litwin Organizational Change Framework
McKinsey's 7S Design Model evaluates organizational effectiveness. It addresses key factors: strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff, and skills. This holistic approach ensures alignment for successful business strategy execution. While providing a comprehensive view of the organization, it may overlook external factors impacting the business environment. Despite its limitations, the model remains a valuable tool for companies seeking to optimize their organizational design and performance. Combining it with other models can offer a more nuanced understanding of the organization's complexity.
Advantages of the Burke Litwin Organizational Change Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model analyzes company culture, structure, and strategy for alignment, making it a pivotal tool in organizational design. Its advantage lies in holistic evaluation, ensuring all aspects harmonize for success. However, limitations include complex implementation and potential resistance to change. Jay Galbraith introduced the Star Model™, emphasizing strategy, structure, processes, rewards, and people as the key elements. This model fosters effective organization design but may face challenges in adapting to dynamic business environments.
Disadvantages of the Burke Litwin Organizational Change Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model assesses alignment within companies. It delves into strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff, and skills, highlighting the complexity of organizations. Advantages include holistic evaluation and a focus on the interconnectedness of elements. However, rigid application may pose challenges in evolving environments. Understanding these nuances aids in effective organizational design, crucial for adapting to the dynamic business world. The model's essence lies in alignment, a cornerstone of successful organizational change.
Experimental models
Some organizations explore cutting-edge approaches like the McKinsey Helix Model and the Holonic Enterprise Model connected through the internet to adapt to the evolving business landscape. These experimental models aim to enhance organizational alignment, optimize workflows, and foster innovation. The McKinsey Helix Model focuses on aligning strategy with organizational structure and processes, while the Holonic Enterprise Model emphasizes collaborative levels within and between organizations. By embracing such innovative models, companies strive to stay ahead in the dynamic and competitive business world.
McKinsey Helix Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model assesses alignment within an organization, covering strategy, structure, systems, shared values, skills, style, and staff. Its strength lies in holistic analysis, ensuring all components support the company's objectives. However, its complexity may overwhelm smaller organizations or those seeking quick fixes. This model is valuable for businesses aiming to optimize performance by refining internal cohesion. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of various elements in achieving organizational success.
Advantages of the Helix Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model is a holistic approach considering Strategy, Structure, Systems, Skills, Shared Values, Style, and Staff. Its advantage lies in analyzing the entire organization for successful change implementation. However, complexity and challenges in quantifying soft elements pose limitations. Jay Galbraith's Star Model™ emphasizes Strategy, Structure, Processes, Rewards, and People. This model aligns business strategy with organization design, enhancing performance. Challenges include the intricate nature and possible resistance to change.
Disadvantages of the Helix Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model offers a holistic view of organizational effectiveness, focusing on seven key elements – strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff, and skills. By aligning these factors, organizations can drive successful change initiatives and enhance overall performance. One advantage of this model is its emphasis on the interconnectedness of components within an organization, fostering a more integrated approach to strategic management. However, a potential drawback is the complexity involved in analyzing and implementing changes across all seven dimensions.
Holonic Enterprise Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model is a holistic approach involving seven interconnected elements for organizational effectiveness. Its strengths lie in its ability to harmonize strategy, structure, systems, shared values, skills, style, and staff within a company. However, the 7S Model may face challenges in dynamic environments where rapid changes occur. Jay Galbraith's Star Model™ focuses on strategy, structure, processes, rewards, and people, emphasizing alignment for success. This model's advantage lies in its comprehensive perspective on organizational design.
The Global Inter-Enterprise Collaborative Level
McKinsey's 7S Design Model examines alignment within an organization, focusing on strategy, structure, systems, and shared values. It enhances understanding of internal dynamics, aiding in successful change implementation. However, it can be complex to apply universally. Jay Galbraith's Star Model™ emphasizes strategy, structure, processes, rewards, and people. It offers a holistic view but may oversimplify complexities. Weisbord's Six Box Model targets clarity, leading to improved organizational effectiveness. It promotes a systemic approach but might overlook interdependencies.
The Intra-Enterprise Level
McKinsey's 7S Design Model analyzes alignment within organizations, focusing on strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff, and skills. It aids in assessing how well elements work together to achieve goals. However, drawbacks include complexities in implementation and potential resistance from employees. Jay Galbraith's Star Model emphasizes the interconnectedness of strategy, structure, processes, rewards, and people. Its strength lies in its holistic approach, yet it may lack flexibility for rapid organizational changes.
The Machine (Physical Agent) Level
McKinsey's 7S Design Model analyzes organizational effectiveness through various interrelated elements like strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff, and skills. Its advantage lies in providing a holistic view of organizational alignment. However, limitations may arise due to its complexity and potential resistance to change within the hierarchy. Jay Galbraith's Star Model™ emphasizes strategy, structure, processes, rewards, and people. While offering clarity in alignment, its rigidity and lack of flexibility could hinder adaptability in dynamic business environments.
The Flexible Organization Model
One popular approach to modern organizational design, often referred to as organization design within the Flexible Organization Model, emphasizes adaptability and agility, allowing companies to quickly respond to changes in the business world. By promoting flexibility within the organizational structure, this model enables a more dynamic response to new business strategies and market demands. In a rapidly evolving environment, the Flexible Organization Model empowers companies to stay ahead of the curve and navigate uncertainties with greater ease.
Advantages of the Flexible Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model focuses on aligning key aspects of an organization for effectiveness. Its strength lies in holistic analysis, addressing strategy, structure, systems, and more. However, its rigid framework may hinder adaptability to rapid changes within the business world. Jay Galbraith's Star Model™ emphasizes strategy, structure, processes, rewards, and people as interdependent factors shaping an organization. This model encourages creating alignment across these elements for improved performance and organizational agility.
Disadvantages of the Flexible Model
McKinsey's 7S Design Model, a comprehensive tool, emphasizes the importance of alignment within organizations. It considers strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff, and skills for effective organizational performance. The model ensures that all elements work together harmoniously to achieve common goals. However, its rigid framework may limit flexibility in dynamic environments. Despite this drawback, the 7S Model remains a valuable resource for companies seeking organizational excellence. It's a guiding light for organizations navigating change and optimizing their structure.
Conclusion
Organizational modeling is an essential aspect of business analysis, helping organizations to structure their operations and achieve their goals effectively. With the right organizational model in place, businesses can streamline processes, optimize resources, and improve outcomes for all stakeholders.
As we have seen throughout this article, a business can choose from different types of organizational models depending on its needs. The functional model focuses on departmental specialization, while the market-oriented model emphasizes customer satisfaction. The matrix model offers a hybrid approach that combines elements of both models.
Developing an effective organizational model requires careful planning and evaluation of various factors, such as company culture and industry trends. As a business analyst or consultant who wants to help companies succeed in today's competitive landscape, it is crucial to understand these factors fully.
Organizational modeling is key for any organization seeking growth and success in today's business world. By understanding what it entails and why it matters so much in modern-day business practices, along with the different types available, plus how best you could go about developing one, you'll be well-equipped enough to steer your organization towards achieving its strategic objectives without fail!
What are the different models of organization?
Different models of organization include the functional model, divisional model, matrix model, and flatarchy model. Each of these models has its own structure and advantages depending on the organization's goals, size, and industry. Choosing the right model is crucial for effective organizational functioning.
CBAP ECBA CCBA
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

State Modeling For Business Analysts - A Beginner’s Guide

Business Analyst Training in 2025 | 100% Success Guarantee


Comments (16)